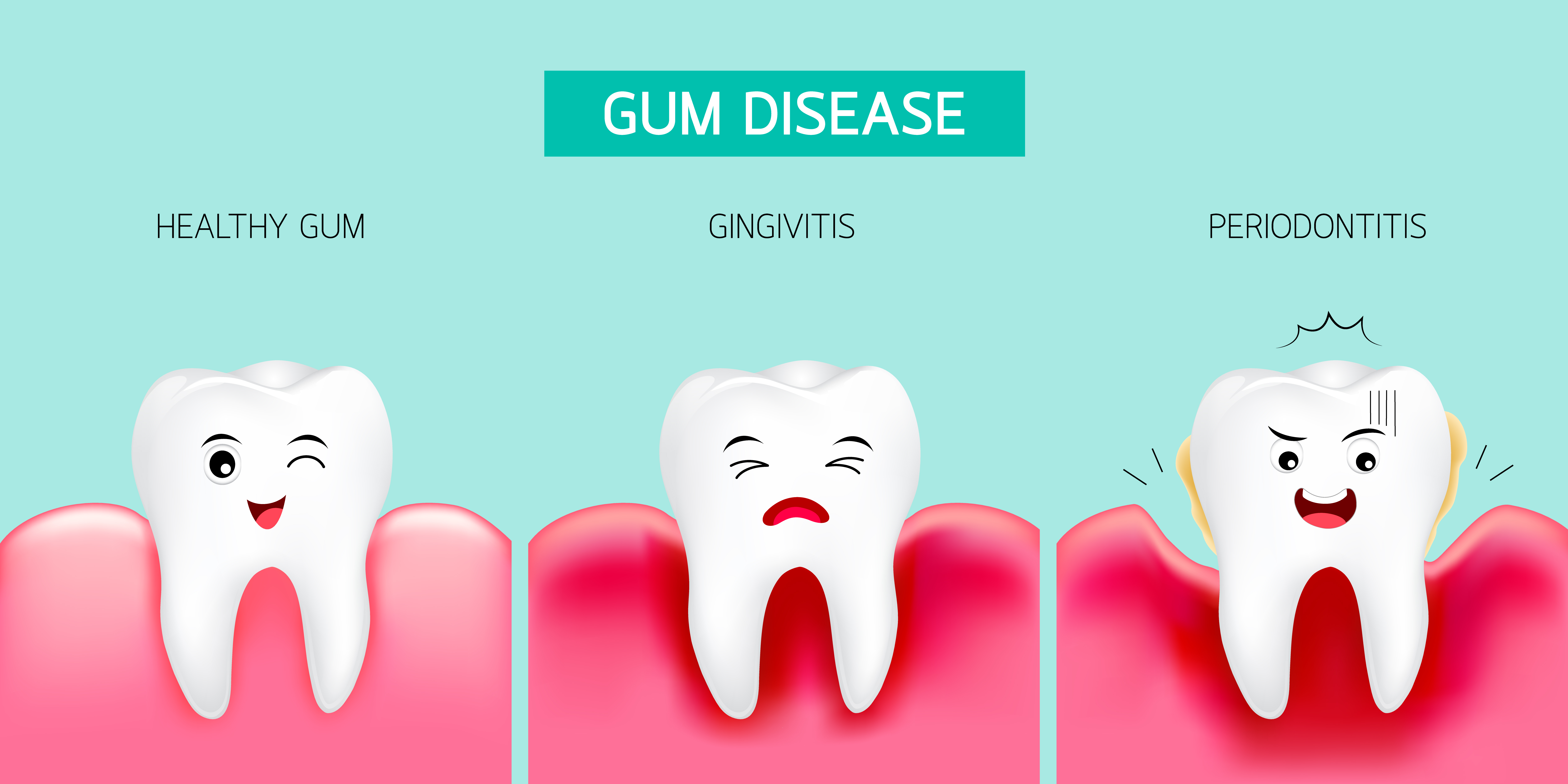
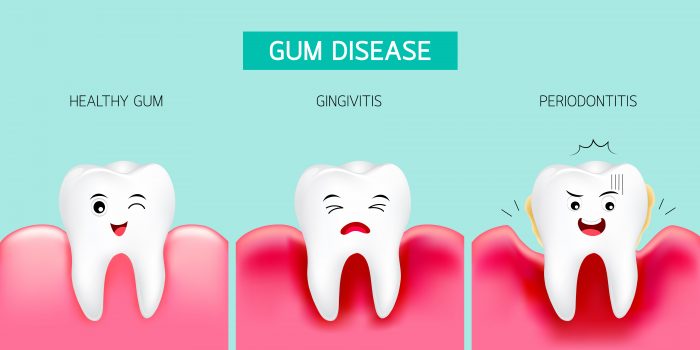
What Is Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is a severe gum disease that damages the tissue and weakens the bone that supports the tooth. Periodontitis can lead to tooth loss and tooth loosening. Periodontitis is one of the most common human diseases; This is caused by a bacteria known as the Periodontal bacteria. These bacterias are always present in the mouth, but poor dental hygiene gives them a chance to grow and multiply.
Periodontal is the more severe stage of the disease Gingivitis. Gingivitis starts with the inflammation of the gum. It is easy to detect if one is suffering from gingivitis. There will be bleeding in the gums indicating that the gum is damaged.

What Are The Causes Of Periodontitis?
There are over 700 bacteria present in a healthy mouth; these bacteria are not harmful to one if the dental hygiene is maintained. But these bacteria are quick to attack an unhealthy mouth.
Bacteria which form dental plaque causes periodontitis. If the plaque is not eliminated the bacteria deposits minerals over a period called tartar. Tartar enhances bacterial growth towards the root. The immune system of the body responds to the bacterial growth leading towards an inflammation of the gums. The gums and roots get detached over time forming a gap known as the Periodontal gap. This gap gives the bacteria more space to multiply, which release toxins that damage the gums and supporting bone structures.
Apart from bacteria formation, there is a host of reason which can lead to periodontitis:
- Smoking and tobacco use: Smoking increases the risk of gum diseases. Smoking is, in fact, one of the primary reasons for periodontitis. Smokers tend to collect a lot of tartar on their teeth, which deepens the periodontal pockets, leaving more space for the bacteria to multiply.
- Braces, misaligned teeth or bridgework: If you cannot brush your teeth properly, you are more likely to get gum disease. When your teeth are misaligned or have braces, it is difficult to brush or floss your teeth properly. Poor brushing increases plaque and tartar in the teeth; This increases the risk of gum diseases.
- Diseases: Certain diseases also may lead to causing periodontitis. Diseases like diabetes can risk the gum disease. Other than diabetes HIV infection or rheumatoid arthritis can also lead to periodontitis.
- Lack of Vitamin C: Lack of vitamin C can cause bleeding and inflamed gums.
What Are The Symptoms Of Periodontitis?
Periodontitis is not a very noticeable condition in the early stages. Its symptoms include:
- Bleeding gums while brushing or flossing.
- Bad breath.
- Teeth are loosening or loss.
- Red, tender and swollen gums.
- Tartar and plaque buildup, visible.
- Pain.
- Continuous foul taste in the mouth.
How To Prevent Periodontitis?
Periodontal disease is a preventable condition. Bacteria present in the mouth don’t attack a healthy mouth. Here are some of the measures that can be taken to prevent periodontitis:
- Brushing teeth: Brushing teeth regularly twice a day is crucial. Brushing removes all food debris and plaque stuck between your teeth and gums. While brushing, tongue cleaning is also essential as bacterias reside there too.
- Floss: Flossing helps clean the areas of the mouth where the brush cannot reach.
- Mouthwash: Rinsing your mouth with mouthwash removes the food particles and plaque that the brush and the floss could not clean.
How To Treat Periodontitis?
Depending on the seriousness of the disease, periodontitis can be treated in two ways. The surgical and the non-surgical approach. If the periodontitis isn’t advance, dentists opt for the non-surgical way. The treatments include:
- Scaling: This process removes the tartar and the bacteria from the tooth and beneath the gums. Laser and ultrasonic devices are used to perform this.
- Antibiotics: Antibiotics can help control bacterial infection. These may include antibiotic mouth rinses, gels, etc.
Advanced periodontitis may require surgical treatments like
- Soft tissue grafts: This method is conducted to reinforce the damaged soft tissues due to gum loss and receding of the gum line; This helps to reduce further gum recession and gives the teeth more pleasing appearance.
- Bone grafting: This process is done when the periodontitis has destroyed the bone surrounding the tooth root. This graft is composed of the fragments of your bone sometimes or by the bone of the donor. This procedure helps prevent tooth loss as it holds the tooth in one place.
Woodbridge Dentist, Dr. April Toyer, suggests visiting the nearest dentist in case any signs of periodontitis is noticed.